
Even if you aren’t very much into cybersecurity and are not particularly tech-savvy, you’ve probably heard about the term phishing. But, do you know how it works and what the most common forms of phishing are?
It’s estimated that around 15 billion spam emails are sent out daily. More worryingly, on average, one in every 99 emails is a phishing attack, meaning that the overall attack rate is just over 1%.
And, to add to this, around 90% of all breaches occur due to phishing. All of these numbers speak to just how important it is to know how phishing works and what the best protection practices against it are.
In this detailed page, we’ll go over various forms of phishing, the differences between them and share with you examples of phishing emails to help you understand everything you need to know about this cybersecurity threat.
What Does Phished Mean?
The first step in protecting against phishing is understanding what it is and how it works. So, what is the meaning of phished, and how do you get phished? In simple terms, phishing is a form of social engineering attack attackers employ to steal your personal data.
In its essence, phishing is a very simplistic form of attack. It revolves around tricking the target victim by impersonating a trustworthy source. Trusting the sender, the victim unknowingly infects their device with malware, freezes their system, or shares sensitive information they wouldn’t reveal to strangers.
Depending on the severity of the phishing attack, there could be very serious consequences for the victim. The target might experience identity theft or lose all of their money. When it comes to who the targets are, anyone can fall prey to such an attack. Moreover, phishing doesn’t only affect individuals. It’s also a common occurrence in the business world.
What is Email Phishing?
Most phishing attacks are carried out through emails, so it’s key to highlight this method in order to help you recognize it. The process is fairly simple. Email phishing techniques involve attackers registering fake domains and creating fake credentials that resemble those coming from legitimate sources.
For example, you might get an email impersonating your bank’s support agent or a representative urging you to change your password, click on a link to fill out some information, or simply download some attachments featuring the latest updates.
Many unsuspecting people assume that, just because the email seems to come from a recognizable address, it’s safe to interact with. However, to avoid getting phished through an email link or attachment, always make sure to double-check the sender’s email address and make sure the email is genuine.
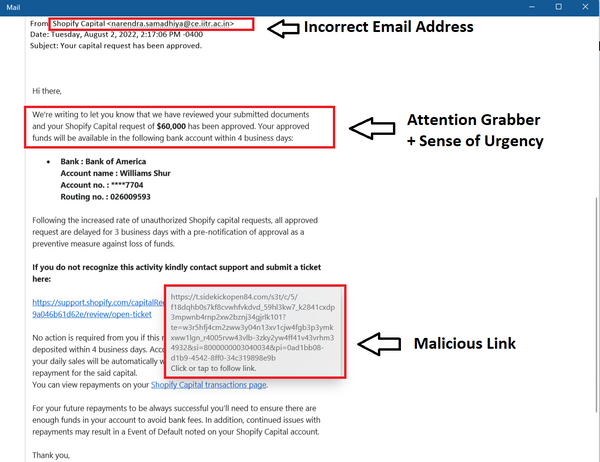
Example of Phishing Attack
While this phishing example is the most common one that affects online users, there are many other types of phishing that you should be aware of. To help you recognize other prevalent types of phishing, let’s quickly highlight them:
- Smishing- this form of phishing replaces email communication with SMS. It involves the cyber attackers sending the victim a similarly-crafted message with a link or attachment, urging them to click on the content of the SMS.
- Vishing - like the previous form of phishing, this includes targeting the victim’s phone, but this time through a voice message. The attackers leave voice messages trying to induce the victim to reveal valuable personal or financial information.
- Angler Phishing - Angle phishing has become increasingly prevalent in today’s era of social media. Attackers disguise themselves as company representatives or customer service agents to obtain personal info, account credentials, or other data of other social media users.
What's Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a more sophisticated type of phishing. Unlike regular phishing, which usually casts a broader net in hopes of capturing a victim, spear phishing is much more targeted. So, in the context of spear phishing vs phishing, the latter focuses more on quantity. While phishing attacks often interact with thousands of recipients, spear phishing attacks don’t come anywhere near this number.
Instead, spear phishing attacks target you as an individual. Prior to sending you a spear phishing email, attackers engage in social engineering, trying to dig up as much information on you as possible to make it seem like they know you.
With this in mind, spear phishing attacks are most often targeting a very specific goal. Most often, they present themselves as someone from your business or personal life, asking you to send them money and forwarding you seemingly genuine wiring instructions.
Whaling vs Spear Phishing vs Phishing
Besides spear phishing, there’s an even more targeted type of attack, called whaling. This form of phishing only targets CEOs and employees at high levels in the corporate world. Whaling attacks often require the attackers to do extensive research and preparation in order to tailor the phishing email to have the best chance of success.
In short, whaling attacks work identically to regular phishing ones, just with a more specific pretext. For instance, cyber attackers impersonate an employee's boss or colleague and usually ask for a favor or provide them with some sort of opportunity that will entice them to interact with the malicious email.

Example of Phishing Attack
Examples of Phishing Attacks
With phishing being the most common security threat in the online world, there are countless examples of phishing attacks out there. So much so, that even some of the biggest companies in the world aren’t impervious to such threats. With that in mind, we want to share two well-known phishing attacks that have occurred in the past few years.
Just this year, there has been an attack on Microsoft 365 accounts based on AITM (Adversary-in-the-Middle) tactics. The attack was so well-targeted that it even worked on users’ email accounts that had MFA enabled.

Example of Phishing Attack
But, this was far from the only successful big phishing attack in 2022. The renowned US company Cloudflare also experienced a phishing attack when its employees were tricked into entering their work credentials on a phishing site. In less than one minute, at least 76 Cloudflare employees received a phishing text, with many of them falling victim to the ruse.

Example of Phishing Attack
How to Stop a Phishing Attack?
Stopping a phishing attack is challenging, as most people notice what’s happening only when it’s too late. But, there are some prevention methods that you can use to ensure you don’t fall victim to a phishing attack. Here are four best tips on how to prevent a phishing attack:
- Always Verify Before Clicking - this simple tip is very effective for helping you avoid phishing scams. Always think before you click on a link or attachment, and avoid clicking on something you’re not 100% sure about.
- Keep Your Information Private - don’t reveal your private information unless you must. Even when you want to log in or purchase something online, don’t do it through email or SMS links. Go directly to the source site.
- Keep Everything Up to Date - mainstream browsers and antivirus programs regularly put out patches to address new security risks, so make sure not to delay updates when prompted.
- Use a Security Key - security keys that meet FIDO U2F/FIDO2 standards are perhaps the best way to protect yourself from phishing. They automatically recognize the genuine domain and eliminate the need for manually typing passwords.
Protecting Yourself Against Phishing Without Delay
In 2017, Google rolled out a new requirement that completely neutralized phishing attacks on its employees. With well around 140,000 employees, Google hasn’t had any phishing attacks since 2017. This might seem like a logistical miracle, but in reality, it was realized with one simple tweak.
In 2017, all Google employees had to stop using passwords to log in. Even using one-time codes was prohibited. Instead, every Google employee had to start using physical security keys to access their accounts.
A Google spokesperson said Security Keys now form the basis of all account access at Google.“ We have had no reported or confirmed account takeovers since implementing security keys at Google,” the spokesperson said. “Users might be asked to authenticate using their security key for many different apps/reasons. It all depends on the sensitivity of the app and the risk of the user at that point in time.”
Of course, these benefits and security features aren’t only reserved for big tech companies and organizations with massive budgets. Everyone can obtain anti-phishing software free of charge or at a minimal cost and protect themselves from the dangers of phishing attacks.
At Hideez, we have created a cost-effective universal security key that is robust and reliable enough to protect against a variety of attacks. Our Hideez Key 4 can protect you against phishing attacks, MITM attacks, spoofing, and any other type of password-related threat.
Best of all, it doesn’t break the bank, so it’s an approachable solution for small businesses and individual users. For just $49, you will get a complete security solution, combining both hardware and software components. This includes a hardware password manager with an autofill feature, a strong password generator, a security key supporting FIDO/U2F standards, and an RFID key fob.
Knowing the many cybersecurity threats that exist in today’s landscape, you shouldn’t leave your security up to chance. Reach out to us now to request a free trial for enterprises!


